Bomb Threat, Sextortion Spammers Abused Weakness at GoDaddy.com

Credit to Author: BrianKrebs| Date: Wed, 23 Jan 2019 02:44:28 +0000
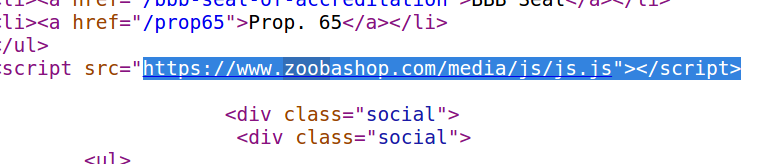
Two of the most disruptive and widely-received spam email campaigns over the past few months — including an ongoing sextortion email scam and a bomb threat hoax that shut down dozens of schools, businesses and government buildings late last year — were made possible thanks to an authentication weakness at GoDaddy.com, the world’s largest domain name registrar, KrebsOnSecurity has learned. Perhaps more worryingly, experts warn this same weakness that let spammers hijack domains registered through GoDaddy also affects a great many other major Internet service providers, and is actively being abused to launch phishing and malware attacks which leverage dormant Web site names currently owned and controlled by some of the world’s most trusted corporate names and brands.
Read More