Ask Fitis, the Bear: Real Crooks Sign Their Malware

Credit to Author: BrianKrebs| Date: Thu, 01 Jun 2023 16:15:34 +0000
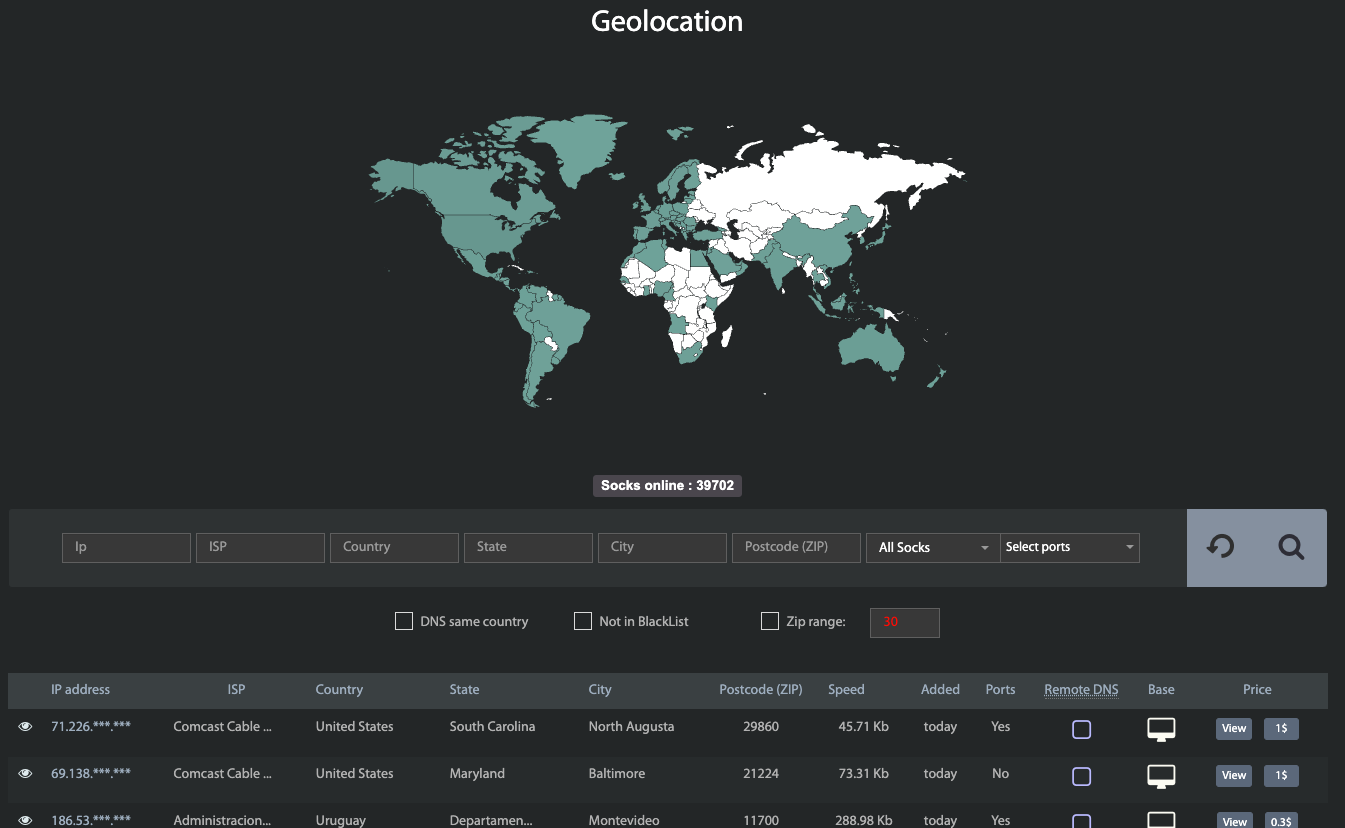
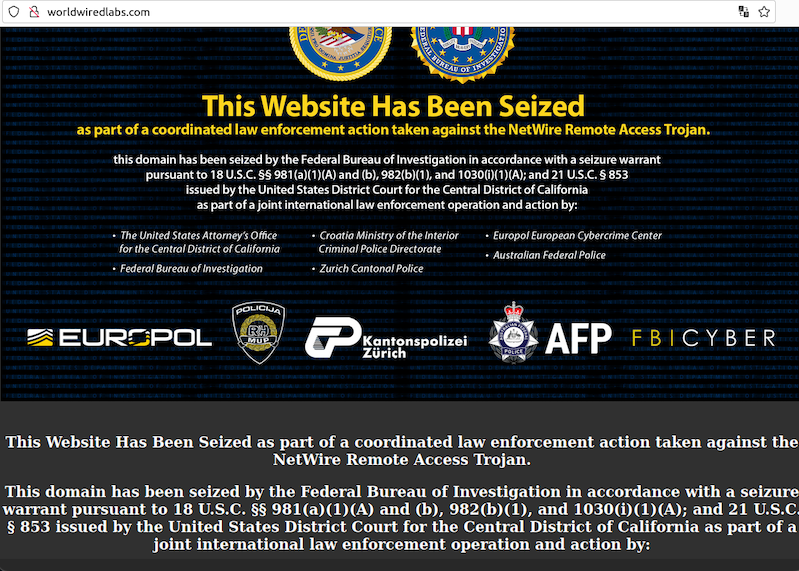
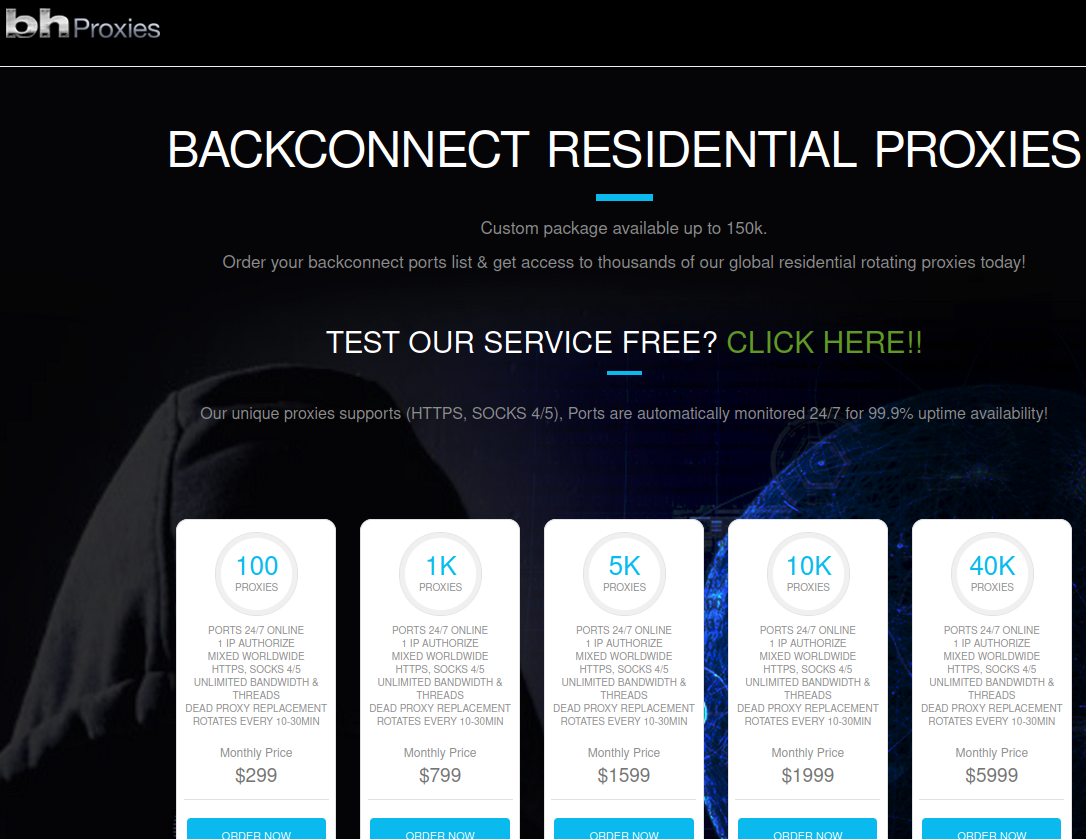
Code-signing certificates are supposed to help authenticate the identity of software publishers, and provide cryptographic assurance that a signed piece of software has not been altered or tampered with. Both of these qualities make stolen or ill-gotten code-signing certificates attractive to cybercriminal groups, who prize their ability to add stealth and longevity to malicious software. This post is a deep dive on “Megatraffer,” a veteran Russian hacker who has practically cornered the underground market for malware focused code-signing certificates since 2015.
Read more